What are the chances of getting cancer in your life? Focus on preventing these five "high-risk cancers"!
Original attention → Health Times
Light the star.
Don’t miss every push.
In life, both cancer patients and healthy people have doubts about the "cancer probability". Many cancer patients will ask, "Why do so many people get cancer?" Healthy people will also worry when they see that people around them find cancer. "So many people with cancer, what is the probability of my cancer?"
Lung cancer screening Shan Mingming photo
In 2018, the global cancer data released by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) pointed out that before the age of 75, the cumulative risk of cancer was 21.4% and the cumulative risk of cancer death was 17.7%. After conversion, about 1/5 of men and 1/6 of women in the world will suffer from cancer in their lifetime. ①
On April 4, 2024, Cancer magazine, a well-known journal in the field of oncology, released the latest global cancer statistics, showing that about one fifth of people will suffer from cancer in their lifetime. ②

This data is basically the same as the "cumulative cancer risk before the age of 75" issued by the International Agency for Research on Cancer. In other words, each of us is about 21.4% likely to get cancer in our lifetime.
Five cancers with the highest number of new cancers and deaths
According to the latest global cancer statistics published by Cancer, a well-known journal in the field of oncology, in 2022, there were 19.96 million new cancer cases and 9.74 million cancer deaths worldwide. The top five cancers with the highest number of new cancers are:
Lung cancer (12.4% of all new cases)
Breast cancer (11.6% of all new cases)
Colorectal cancer (9.6% of all new cases)
Prostate cancer (7.3% of all new cases)
Gastric cancer (4.9% of all new cases)
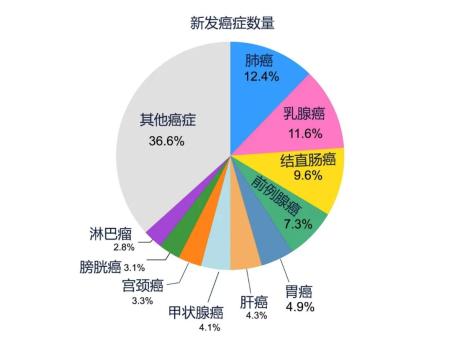
Translated picture of Health Times
At the same time, the top five cancers with the highest number of cancer deaths are:
Lung cancer (18.7% of all cancer deaths)
Colorectal cancer (9.3% of all cancer deaths)
Liver cancer (7.8% of all cancer deaths)
Breast cancer (6.9% of all cancer deaths)
Gastric cancer (6.8% of all cancer deaths)
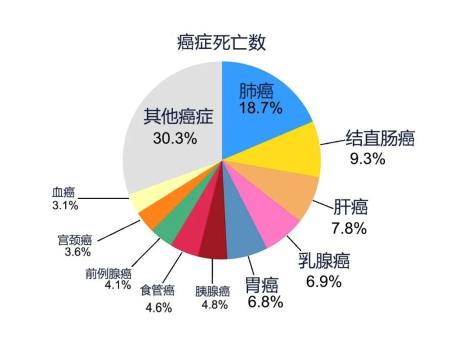
Translated picture of Health Times
Among women, breast cancer is the most common cancer and the leading cause of cancer death. Followed by lung cancer and colorectal cancer;
Among men, lung cancer is the most common cancer, followed by prostate cancer and colorectal cancer, as well as liver cancer and colorectal cancer. ②

Photo by Liu Weihua
Focus on preventing five kinds of "high-risk cancers"
What are the symptoms that need attention in the early stage? How to prevent it? According to the "Guidelines for Cancer Prevention and Screening (Popular Science Edition)" compiled by the Disease Prevention and Control Bureau of the National Health and Wellness Commission and the National Cancer Center, about 45% of cancers in China can be effectively prevented by changing unhealthy lifestyles, avoiding exposure to cancer-related risk factors and vaccinating preventive vaccines. ③
Lung cancer
[Early symptoms] Most of them have no symptoms; Pay attention to respiratory symptoms such as cough, hemoptysis, chest and back pain and wheezing.
[How to prevent]
1. Control tobacco.
2. Avoid exposure to dangerous factors.
3. Avoid indoor and outdoor air pollution.
4. Cook a range hood, stir fry less and fry less.
[High-risk group]
1. Smoking ≥30 packs a year.
2. Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
3. Have a history of occupational exposure (asbestos, radon, beryllium, uranium, chromium, cadmium, nickel, silicon, diesel exhaust gas, soot and soot) for at least one year.
4. Those who have been passive smokers for more than 20 years, including those who have smoked for more than 30 years and quit smoking for less than 15 years.
[Early screening method] Low dose spiral CT of chest; Those who have no obvious abnormality are reviewed by LDCT once a year.
[breast cancer]
【 Early symptoms 】 Breast lump, nipple discharge, changes in skin characteristics, abnormal nipple areola and axillary lymph node enlargement.
[How to prevent]
1. Practice a healthy lifestyle.
2. Quit smoking and limit alcohol, exercise moderately, eat more vegetables and keep weight.
3. Give birth as soon as possible and advocate breastfeeding.
[High-risk group]
1. Female aged 45-74.
2. The age of menarche is ≤12 years old.
3. Menopause age ≥55 years old.
4. Have a history of breast biopsy or surgery for benign breast diseases.
5. First-degree relatives have a history of breast cancer, or second-degree relatives have two or more people suffering from breast cancer or two or more people suffering from ovarian cancer before the age of 50.
6. Use hormone replacement therapy of "estrogen and progesterone combination" for half a year or more.
7. Use "estrogen" instead of treatment for half a year or more.
8. No breast-feeding history or breast-feeding time less than 4 months.
9. No history of live birth (including never giving birth, abortion or stillbirth) or the age of first live birth ≥30 years old.
[Early screening method] For women aged 45-74, it is recommended to have mammography combined with ultrasound screening every year; Women under the age of 40 who have no clear risk factors for breast cancer or have no abnormalities in clinical examination are not recommended to have breast X-ray examination first.

Health times chart
[colorectal cancer]
【 Early Symptoms 】 The clinical symptoms of early colorectal cancer are not obvious, and the symptoms that need to be guarded include: gastrointestinal bleeding (black stool, bloody stool, etc.), emaciation, diarrhea, abdominal mass, and changes in defecation habits.
[How to prevent]
1. Insist on physical exercise to avoid obesity.
2. Healthy diet, increase the intake of crude fiber and fresh fruit, and avoid high-fat and high-protein diet.
3. Quit smoking and limit alcohol to avoid its long-term inflammatory stimulation to the digestive tract.
[High-risk group]
1. male.
2. Age ≥45 years old.
3. Smokers (including those who have quit smoking).
4. Body mass index ≥24.
5. History of colorectal polyps.
6. Family history of colorectal cancer in first-degree relatives.
7. Suffering from familial adenomatous polyposis and Lynch syndrome.
[Early screening method] It is recommended that ordinary people aged 45 and above complete the colorectal cancer risk assessment questionnaire at home, and then conduct simple colorectal cancer screening, such as fecal occult blood test.
Prostate cancer
【 Early symptoms 】 Early prostate cancer is mostly confined to the prostate and does not invade the tissues around the prostate, and often has no obvious clinical manifestations.
[How to prevent]
1. Reduce animal fat intake.
2. Drink green tea properly and increase the intake of soybeans, fruits, vegetables and vitamin E.
[High-risk group]
1. Age > 50 years old.
2. Age > 45 years and family history of prostate cancer.
3. Age > 40 years and baseline prostate specific antigen > 1 μ g/L..
[Early screening method] It is recommended that men over 50 years old and in good health have regular physical examinations, and high-risk individuals can have their serum prostate-specific antigen tested once every two years.
[gastric cancer]
【 Early symptoms 】 There are many atypical symptoms in the early stage, and a few have atypical stomach symptoms such as nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite. The common symptoms in the advanced stage are epigastric pain, weight loss, hematemesis or bloody stool.
[How to prevent]
1. Reduce salt intake, eat less pickled, smoked and fried foods, red meat and processed meat, and increase the intake of vegetables and fruits.
2. chew slowly.
3. Quit smoking and limit alcohol.
4. Pay attention to stomach diseases such as gastric intraepithelial neoplasia, chronic atrophic gastritis, gastric polyp, remnant stomach after operation, hypertrophic gastritis and gastrointestinal metaplasia, treat them in time and review them regularly.
5. Timely treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection.
[High-risk group]
1. The older you get, the higher the risk.
2. Helicobacter pylori infection.
3. High-salt diet, smoked fried food, excessive intake of red meat and processed meat.
4. Long-term no breakfast, irregular diet, fast eating, overeating, leftover food, insufficient intake of fruits and vegetables and other bad eating habits.
5. Smoking and drinking.
6. Have a family history of gastric cancer.
7. Suffering from gastroesophageal reflux disease can increase the risk of cardiac cancer, and chronic atrophic gastritis is an important risk factor for non-cardiac gastric cancer.
8. Diabetes, obesity, psychosocial factors and immune factors may also be related to the occurrence of gastric cancer.
[Early screening method] High-risk population of gastric cancer: upper gastrointestinal endoscopy.
More exciting content
be carefully chosen
essay
This article is synthesized from:
①Freddie Bray BSc, et al. Global Cancer Statistics2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in185 Countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. First published: 12September 2018.https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492.
②Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.3322/caac.21834
③ Guidelines for Cancer Prevention and Screening (Popular Science Edition) in February 2021, Bureau of Disease Control and Prevention, National Health Commission, National Cancer Center.
Original title: "What is the probability of cancer in your life? Focus on preventing these five "high-risk cancers"! 》
Read the original text